BP003¶
- Number
BP003
- Title
N(ext)Runner Task Life-Cycle
- Author
Cleber Rosa <crosa@redhat.com>
- Discussions-To
- Reviewers
Beraldo Leal <bleal@redhat.com>, Willian Rampazzo <willianr@redhat.com>
- Created
20-July-2020
- Type
Architecture Blueprint
- Status
WIP
Table of Contents
TL;DR¶
The N(ext) Runner has been used as Avocado’s runner for selftests for
over a year. The implementation used is based on the avocado nrun
command, that is, outside of the Avocado’s traditional avocado run
entrypoint. Under the hood, it means that the N(ext) Runner is not
integrated well enough with an Avocado Job.
A partial implementation of the N(ext) Runner integration with an
Avocado Job is available at avocado/plugins/runner_nrunner.py but
it has a number limitations.
The N(ext) Runner executes tests as Tasks. This blueprint describes the phases
that a Task can be in throughout its life-cycle, and how the handling
of these phases or states, will power the tests execution mechanism
within the context of an Avocado Job.
Motivations¶
Propose an architecture for integrating the N(ext) Runner concepts and features into an Avocado Job. Because the N(ext) Runner contains distinguishing features that the original Avocado Job did not anticipate, a proxy layer is necessary.
The current runner (and Job) is built on the premises that there’s a “currently executing test”, and thus, does not need to keep track of various running tests states at once. The N(ext) Runner, on the other hand, support for running tests in parallel, and thus needs supporting code for keeping track of their state and forward their relevant information to an Avocado Job.
Goals of this BluePrint¶
Propose an architecture based on the life-cycle phases that an N(ext) Runner Task can go through while running under an Avocado Job.
Describe how the proposed architecture can power an implementation suitable for the next Avocado LTS release (82.0), having feature completeness when compared to the current runner, while still making its distinguishing features available to users who opt in. This also means that the current Avocado Job interface will continue to support the current runner implementation.
Prove that the current runner can be removed without significant user impact after the LTS release (within the 83.0 development cycle), based on the feature completeness of the N(ext) Runner with regards to its integration with an Avocado Job.
Allow for future extension of the Task life-cycle phases architecture, such as into a more capable and further reaching scheduler for Tasks. This means that this BluePrint is focused on short term integration issues, as describe in the motivation, but at the same tries to not impose future limitations to have new features implemented for other use cases.
Requirements¶
This section describes the requirements to manage the Task’s life-cycle. It also describes the phases of a Task life-cycle and includes an example.
Task Execution Requirements Verification¶
For a Task to actually be executed, there needs to be a minimal number of requirements present. For instance, it’s pointless to attempt to execute a Task of kind “custom” without either:
An
avocado-runner-customrunner script that is compatible with the Avocado interface, ORA
CustomRunnerrunner class that is compatible with theavocado.core.nrunner.BaseRunnerinterface
Other types of Task Execution Requirements checks may be added in the future, but the core concept that a Task can not always be executed remains.
Currently, as per the avocado nrun implementation, this
verification is done in a synchronous way, and it’s of limited
visibility to the user.
Requirements:
The verification of one Task’s requirement should not block other Tasks from progressing to other phases.
The user interface should provide more information on tasks that either failed the verification or that still going through the verification process.
Parallelization and Result Events¶
The N(ext) Runner allows for the parallel execution of tasks. When integrated into a Job, it means there can be more than one test running at a given time.
Currently, plugins that implement the
avocado.core.plugin_interfaces.ResultEvents interface may
contain logic that assumes that the same test will have
start_test, test_progress and then end_test methods called
in that particular order, and only then another test will have any of
those called on its behalf.
For instance, the Human UI plugin will currently:
Print a line such as
(1/1) /bin/true:when a test starts, that is, whenavocado.core.plugin_interfaces.ResultEvents.start_test()is called.Add a throbber and/or change its state whenever a progress update is received, that is, when
avocado.core.plugin_interfaces.ResultEvents.test_progress()is called.Add a test result such as
PASS (0.01 s)when the test finishes, that is, whenavocado.core.plugin_interfaces.ResultEvents.end_test()is called.
Other implementations, such as the TAP result plugin, will only print a line when the final test result is known.
Requirement: have no conflicts of test information when more than one is running in parallel.
Requirement example: provide the test progress notification and the final test result information “in line” with the correct test indication (if given earlier).
Note
Ideally, this shouldn’t require a change to the interface, but only within the implementation so that the presentation of coherent test result events is achieved.
Non-blocking Parallelization¶
As stated earlier, the N(ext) Runner allows for the parallel execution of tasks. A given Task should be allowed to be executed as early as possible, provided:
Its requirements (such as its specific test runners) are available.
A limit for concurrently running tasks has not been reached.
Requirement: there should be no artificial and unnecessary blocking of the parallelization level.
Requirement example: if an hypothetical Result Events plugin interacts with a high latency server, and such interaction takes 2 minutes, the execution of new tasks should not be affected by it.
Note
There are a number of strategies for concurrent programming in Python these days, and the “avocado nrun” command currently makes use of asyncio to have coroutines that spawn tasks and collect results concurrently (in a preemptive cooperative model). The actual tools/libraries used in the implementation shall be discussed later.
Passive Task Status Collection¶
The N(ext) Runner architecture allows tests to run in a much more decoupled way, because of a number of its characteristics, including the fact that Tasks communicate their status by sending asynchronous messages.
Note
The current implementation uses network sockets as the transport for these messages, in part for its universal aspect, and in part to enforce this decoupling. Future implementations may provide alternate transports, such as file descriptors, serial connections, etc.
There currently is a component used for a similar role used in
avocado nrun: avocado.core.nrunner.StatusServer, but it
exceeds what’s needed here in some aspects, and lacks in others
aspects.
Requirement: have a mechanism that can receive and collect in an organized manner, all the state messages coming from tasks that are part of an Avocado Job.
Requirement example: the Avocado Job should be able to use the collection of task status information to ask questions such as the following.
When was the last time that task “123-foobar” gave an status update? Such information would be useful to determine if the task should be abandoned or destroyed as part of a timeout handling, as described in the later section about Task Monitoring and Termination.
Has the task “123-foobar” given a final status update? That is, can we conclude that, as a Task, regardless of the success or failure of what it ran, it finished its execution? Such information would be useful to post the final test result to the Job results and
ResultEventplugins, as described in the next section.
Proxy from Task Status To Job Result¶
An Avocado Job contains an avocado.core.result.Result which
tallies the overall job results. But, the state messages coming from
Tasks are not suitable to being given directly to methods such as
avocado.core.result.Result.check_state(). A mechanism is needed
to proxy and convert the relevant message and events to the current
Avocado job result and ResultEvents plugins.
Requirements:
Proxy Task Status messages and convert them into the appropriate information suitable for
avocado.core.result.Result.Allow
ResultEventsplugins to act as soon as possible on relevant status messages;
Task Monitoring and Termination¶
The N(ext) Runner architecture, as stated before, can have tasks running without much, if any, contact with an Avocado Job. But, an Avocado Job must have a beginning and end, and with that it’s necessary to monitor tasks, and if their situation is not clear, decide their fate.
For instance, a Task started as part of an Avocado Job may communicate the following messages:
{'status': 'started', 'time': 1596680574.8790667, 'output_dir': '/tmp/.avocado-task-d8w0k9s1', 'id': '1-/bin/sleep'}
{'status': 'running', 'time': 1596680574.889258, 'id': '1-/bin/sleep'}
Then it may go offline for eternity. The possible reasons are varied, and despite them, the Job will eventually have to deal the non-final, unknown state of tasks and given them a resolution.
Note
The Spanwer may be able to provide additional information that will help to decide the handling given to such as Task (or its recorded final status). For instance, if a Task running on a container is not communicating its status, and its verified that the container has finished its execution, it may be wise to not wait for the timeout.
Requirements:
Monitor the execution of a task (from an external PoV).
Unless it proves to be, say because of complexity or impossibilities when interacting with the spawners, tasks that are unresponsive should attempt to be terminated.
Notify the user if stray tasks should be clean up manually. This may be, for instance, necessary if a Task on a container seems to be stuck, and the container can not be destroyed. The same applies to a process in an uninterruptible sleep state.
Update Job result with the information about monitored tasks.
Note
Tasks going through the usual phases will end up having their final state in the going through the task status collection described earlier, and from there have them proxied/converted into the Job result and plugins. At first sight, it seems that the task monitoring should use the same repository of status and update it in a similar way, but on behalf of the “lost/exterminated task”.
Suggested Terminology for the Task Phases¶
Task execution has been requested¶
A Task whose execution was requested by the user. All of the tasks on a Job’s
test_suite attribute are requested tasks.
If a software component deals with this type of task, it’s advisable that it
refers to TASK_REQUESTED or requested_tasks or a similar name that links
to this definition.
Task is being triaged¶
The details of the task are being analyzed, including, and most
importantly, the ability of the system to run it. A task that leaves
triage, and it’s either considered FINISHED because it can not be
executed, or is READY and waits to be executed.
If a software component deals with this type of task, for instance, if a “task
scheduler” is looking for runners matching the Task’s kind, it should keep it
under a tasks_under_triage or mark the tasks as TASK_UNDER_TRIAGE or
TASK_TRIAGING a similar name that links to this definition.
Task is ready to be started¶
Task has been triaged, and as much as the system knows, it’s ready to be executed. A task may be in this phase for any amount of time, given that the capacity to have an additional task started is dynamic and may be enforced here.
If a software component deals with this type of task, it should keep
it under a tasks_ready or mark the tasks as TASK_READY or a
similar name that links to this definition.
Task has been started¶
A task was successfully started by a spawner.
Note that it does not mean that the test that the task runner (say,
an avocado-runner-$kind task-run command) will run has already
started. This will be signaled by a runner, say
avocado-runner-$kind producing an status: started kind of
status message.
If a software component deals with this type of task, it should keep
it under a tasks_started or mark the tasks as TASK_STARTED or
a similar name that links to this definition.
Task is finished¶
This means that there’s no longer any activity or a new phase for this task to move to.
It’s expected that extra information will be available explaining
how/why the task arrived in this phase. For instance, it may have
come from the TASK_TRIAGING phase and never gone through the
TASK_STARTED phase. Alternatively, it may been in the
TASK_STARTED phase and finished without any errors.
It should be kept under a tasks_finished structure or be marked as
TASK_FINISHED or a similar name that links to this definition.
Note
There’s no associated meaning here about the pass/fail output of the test payload executed by the task.
Task life-cycle example¶
A task will usually be created from a Runnable. A Runnable will, in turn, almost always be created as part of the “avocado.core.resolver” module. Let’s consider the following output of a resolution:

Two Runnables here will be transformed into Tasks. The process usually includes adding an identification and a status URI:
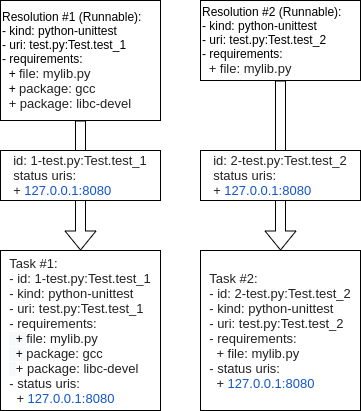
In the end, a job will contain a test_suite with “Task #1” and “Task #2”. It
means that the execution of both tasks was requested by the Job owner.
These tasks will now be triaged. A suitable implementation will move those tasks
to a tasks_under_triage queue, mark them as TASK_UNDER_TRIAGE or some other
strategy to differentiate the tasks at this stage.
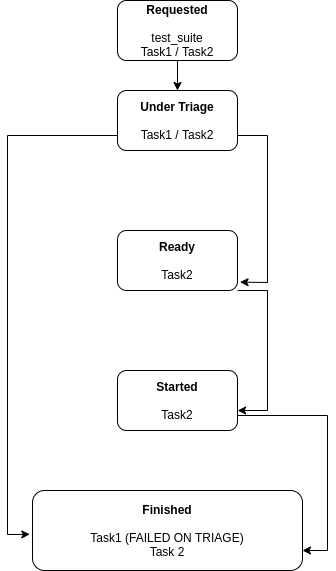
Iteration I¶
Task #1 is selected on the first iteration, and it’s found that:
A suitable runner for tasks of kind
python-unittestexists;The
mylib.pyrequirement is already present on the current environment;The
gccandlibc-develpackages are not installed in the current environment;
Task #1 is not ready to be executed, so it’s moved to
TASK_FINISHED and it’s reason is recorded.
No further action is performed on the first iteration because no other relevant state exists (Task #2, the only other requested task, has not progressed beyond its initial stage).
Iteration II¶
On the second iteration, Task #2 is selected, and it’s found that:
A suitable runner for tasks of kind
python-unittestexists;The
mylib.pyrequirement is already present on the current environment.
Task #2 is now ready to be started.
As a reminder, Task #1 has not passed triaging and is TASK_FINISHED.
Iteration III¶
On the third iteration, there are no tasks left under triage, so the action is now limited to tasks being prepared and ready to be started.
Note
As an optimization, supposing that the “status uri” 127.0.0.1:8080, was set by the job, as its internal status server, it must be started before any task, to avoid any status message being lost. Without such an optimization, the status server could be started earlier.
At this stage, Task #2 has been started.
Final Iteration¶
On the fifth iteration, the spawner reports that Task #2 is not alive anymore, and the status server has received a message about it.
Because of that, Task #2 is now considered TASK_FINISHED.
Tallying results¶
The nrunner plugin should be able to provide meaningful results to the Job, and consequently, to the user, based on the resulting information on the final iteration.
Notice that some information, such as the PASS for the second test,
will come from the “result” given in a status message from the task
itself. Some other status, such as the CANCEL status for the
first test will not come from a status message received, but from a
realization of the actual management of the task execution. It’s
expected to other information will also have to be inferred, and
“filled in” by the nrunner plugin implementation.
In the end, it’s expected that results similar to this would be presented:
JOB ID : f59bd40b8ac905864c4558dc02b6177d4f422ca3
JOB LOG : /home/user/avocado/job-results/job-2020-05-20T17.58-f59bd40/job.log
(1/2) tests.py:Test.test_1: CANCEL (0 s)
(1/2) tests.py:Test.test_2: PASS (2.56 s)
RESULTS : PASS 1 | ERROR 0 | FAIL 0 | SKIP 0 | WARN 0 | INTERRUPT 0 | CANCEL 1
JOB TIME : 0.19 s
JOB HTML : /home/user/avocado/job-results/job-2020-05-20T17.58-f59bd40/results.html
Notice that Task #2 may show up before Task #1. There may be issues associated with the current UI to deal with regarding out of order task status updates.
Implementation Example¶
The following implementation example uses random sleeps and random (but biased) results from operations expected to happen on different phases, to simulate the behavior of real tasks.
The enforcement of some artificial limits (such as the number of tasks
TASK_STARTED) is also exemplified. As a general rule, all tasks
are attempted to be moved further into their life-cycle and a number
of “workers” doing that should not conflict with each other.
This implementation uses Python’s asyncio library very crudely.
The final implementation may use other tools, such as a
asyncio.Queue instead of plain lists with a
asyncio.Lock. It may also use individual Tasks for each work in each phase.
import asyncio
import itertools
import random
import time
from avocado.utils.astring import tabular_output
DEBUG = False
def debug(msg):
if DEBUG:
print(msg)
async def sleep_random():
await asyncio.sleep(random.random())
def true_or_false(handicap=3):
"""Returns a random positive or negative outcome, with some bias."""
if handicap > 1:
choices = [True] + ([False] * handicap)
else:
choices = [False] + ([True] * abs(handicap))
return random.choice(choices)
def mock_check_task_requirement():
# More success than failures, please
return true_or_false(-8)
def mock_check_task_start():
# More success than failures, please
return true_or_false(-6)
def mock_monitor_task_finished():
# More failures than successes, please
return true_or_false(5)
class Task:
"""Used here as a placeholder for an avocado.core.nrunner.Task."""
def __init__(self, identification):
self._identification = identification
class TaskInfo(Task):
"""Task with extra status information on its life-cycle.
The equivalent of a StatusServer will contain this information
in the real implementation."""
def __init__(self, identification):
super().__init__(identification)
self._status = None
self._timeout = None
@property
def status(self):
return self._status
@status.setter
def status(self, status):
self._status = status
@property
def timeout(self):
return self._timeout
@timeout.setter
def timeout(self, timeout):
self._timeout = timeout
def __repr__(self):
if self._status is None:
return f"{self._identification}"
else:
return f"{self._identification} ({self.status})"
class TaskStateMachine:
"""Represents all phases that a task can go through its life."""
def __init__(self, tasks):
self._requested = tasks
self._triaging = []
self._ready = []
self._started = []
self._finished = []
self._lock = asyncio.Lock()
@property
def requested(self):
return self._requested
@property
def triaging(self):
return self._triaging
@property
def ready(self):
return self._ready
@property
def started(self):
return self._started
@property
def finished(self):
return self._finished
@property
def lock(self):
return self._lock
@property
async def complete(self):
async with self._lock:
pending = any([self._requested, self._triaging, self._ready, self._started])
return not pending
def __str__(self):
headers = (
"|_REQUESTED_|",
"|_TRIAGING__|",
"|___READY___|",
"|__STARTED__|",
"|______FINISHED_______|",
)
data = itertools.zip_longest(
self._requested,
self._triaging,
self._ready,
self._started,
self._finished,
fillvalue="",
)
matrix = [_ for _ in data]
return tabular_output(matrix, headers)
async def bootstrap(lc):
"""Reads from requested, moves into triaging."""
# fake some rate limiting
if true_or_false(10):
return
try:
async with lc.lock:
task = lc.requested.pop()
lc.triaging.append(task)
debug(f"Moved Task {task}: REQUESTED => TRIAGING")
except IndexError:
debug("BOOTSTRAP: nothing to do")
return
async def triage(lc):
"""Reads from triaging, moves into either: ready or finished."""
await sleep_random()
try:
async with lc.lock:
task = lc.triaging.pop()
except IndexError:
debug("TRIAGE done")
return
if mock_check_task_requirement():
async with lc.lock:
lc.ready.append(task)
debug(f"Moving Task {task}: TRIAGING => READY")
else:
async with lc.lock:
lc.finished.append(task)
task.status = "FAILED ON TRIAGE"
debug(f"Moving Task {task}: TRIAGING => FINISHED")
async def start(lc):
"""Reads from ready, moves into either: started or finished."""
await sleep_random()
try:
async with lc.lock:
task = lc.ready.pop()
except IndexError:
debug("START: nothing to do")
return
# enforce a rate limit on the number of started (currently running) tasks.
# this is a global limit, but the spawners can also be queried with regards
# to their capacity to handle new tasks
MAX_RUNNING_TASKS = 8
async with lc.lock:
if len(lc.started) >= MAX_RUNNING_TASKS:
lc.ready.insert(0, task)
task.status = "WAITING"
return
# suppose we're starting the tasks
if mock_check_task_start():
async with lc.lock:
task.status = None
# Let's give each task 15 seconds from start time
task.timeout = time.monotonic() + 15
lc.started.append(task)
debug(f"Moving Task {task}: READY => STARTED")
else:
async with lc.lock:
lc.finished.append(task)
task.status = "FAILED ON START"
debug(f"Moving Task {task}: READY => FINISHED (ERRORED ON START)")
async def monitor(lc):
"""Reads from started, moves into finished."""
await sleep_random()
try:
async with lc.lock:
task = lc.started.pop()
except IndexError:
debug("MONITOR: nothing to do")
return
if time.monotonic() > task.timeout:
async with lc.lock:
task.status = "FAILED W/ TIMEOUT"
lc.finished.append(task)
debug(f"Moving Task {task}: STARTED => FINISHED (FAILED ON TIMEOUT)")
elif mock_monitor_task_finished():
async with lc.lock:
lc.finished.append(task)
debug(f"Moving Task {task}: STARTED => FINISHED (COMPLETED AFTER STARTED)")
else:
async with lc.lock:
lc.started.insert(0, task)
debug(f"Task {task}: has not finished yet")
def print_lc_status(lc):
print("\033c", end="")
print(str(lc))
async def worker(lc):
"""Pushes Tasks forward and makes them do something with their lives."""
while True:
complete = await lc.complete
debug(f"Complete? {complete}")
if complete:
break
await bootstrap(lc)
print_lc_status(lc)
await triage(lc)
print_lc_status(lc)
await start(lc)
print_lc_status(lc)
await monitor(lc)
print_lc_status(lc)
if __name__ == "__main__":
NUMBER_OF_TASKS = 40
NUMBER_OF_LIFECYCLE_WORKERS = 4
tasks_info = [
# pylint: disable=C0209
TaskInfo("%03i" % _)
for _ in range(1, NUMBER_OF_TASKS - 1)
]
state_machine = TaskStateMachine(tasks_info)
loop = asyncio.get_event_loop()
workers = [
loop.create_task(worker(state_machine))
for _ in range(NUMBER_OF_LIFECYCLE_WORKERS)
]
loop.run_until_complete(asyncio.gather(*workers))
print("JOB COMPLETED")
Backwards Compatibility¶
The compatibility of the resulting Job compatible runner implementation with the current runner is to be verified by running the same set of “Job API feature tests”, but with this runner selected instead.
There are no compatibility issues with the previous versions of
itself, or with the non-Job compatible nrun implementation.
Security Implications¶
None that we can determine at this point.
How to Teach This¶
The distinctive features that the N(ext) Runner provides should be properly documented.
Users should not be required to learn about the N(ext) Runner features to use it just as an alternative to the current runner implementation.
Future work¶
These are possible future improvements to the Task phases, and may be a partial list of addition towards a more comprehensive “Task scheduler”. They are provided for discussion only and do not constitute hard requirements for this or future work.
Tasks’ requirements fulfillment¶
1. Prepare for the execution of a task, such as the fulfillment of extra task requirements. The requirements resolver is one, if not the only way, component that should be given a chance to act here;
Executes a task in a prepared environment;
Active Task Status Collection¶
Some environments and use cases may require disconnected execution of tasks. In such cases, a Job will have to activelly poll for tasks’ statuses, which may be:
an operation that happens along the task execution.
only at the end of the task execution, as signalled by the termination of the environment in which a task is running on.
References¶
RFC: https://www.redhat.com/archives/avocado-devel/2020-May/msg00015.html
Early implementation: https://github.com/avocado-framework/avocado/pull/3765
Requirement check prototype: https://github.com/avocado-framework/avocado/pull/4015